When Is The Drug Levodopa Used?
Levodopa is a drug that is used to treat Parkinson’s disease. This drug acts on the central nervous system and is converted into dopamine in the brain.
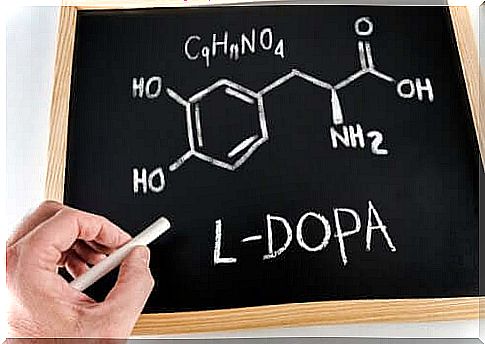
The drug levodopa is a drug from the group of anti-Parkinson drugs that is often prescribed for Parkinson’s disease. In combination with other DOPA decarboxylase inhibitors, such as carbidopa or benserazide, this drug is used in this disease.
The first scientist to link Parkinson’s disease to dopamine deficiency is the biochemist Oleh Hornykiewicz. He examined autopsies of patients with Parkinson’s disease and came to this conclusion. After that, this scientist began treating Parkinson’s patients with a racemic mixture of DOPA. With this he achieved positive results.
A short time later , the scientist Curt Porter was able to prove that the stereoisomer L-DOPA is actually active. This enabled the effective dose of the composition to be reduced by half.
After a while, people began to synthesize various molecules such as benserazide and carbodopa. These improved the results of the treatment. In doing so, the scientists also reduced the dose required to achieve the desired effects.
Different aspects of Parkinson’s disease

Parkinson’s is a central nervous system disease caused by a lack of dopamine in the cells of the corpus striatum as the nigra cells die.
The origin of this disease is multifactorial and its prevalence is relatively high. The elderly suffer most from it. In concrete terms, around 2 percent of people over 65 suffer from Parkinson’s disease. But this disease can also occur at a young age.
One of the most common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease is tremors. Over 60 percent of patients are affected. However, other motor symptoms can also occur. For example:
- stiffness
- Slow movements, also called bradykinesia
- Postural instability (reflexes that can balance the body are disturbed)
Other symptoms that can appear in the course of the disease include:
- Dementia and memory loss
- Hallucinations
- depression
- Dysphagia
- muscle pain
- Neuropathic pain
It is also known that this disease is associated with an increased production of the protein α-synuclein (SNCA). Also in Alzheimer this is the case. Therefore, the therapeutic strategy currently being explored consists of the administration of aggregation inhibitors for α-synuclein or the immunization of these protein derivatives. This type of therapy was researched in a study with nilotinib.
General properties of levodopa
In the therapy of Parkinson’s, the dopamine level should be increased by directly addressing the receptors. This is achieved by inhibiting the enzyme AADC, which catalyzes the conversion of dopa into dopamine.
The question arises as to why patients are not receiving dopamine directly. The problem with this is that dopamine given by tablets or injections cannot be absorbed from the blood into the brain. Therefore it remains ineffective. It cannot cross the blood-brain barrier that protects the brain.
For this reason, Parkinson’s is treated with the precursor to dopamine, with levodopa. This active ingredient can cross the blood-brain barrier and is converted into dopamine as soon as it enters the central and peripheral nervous system.
But even if levodopa crosses the blood-brain barrier, this active ingredient has a strong peripheral metabolism, so little of it reaches the brain.
To solve this problem, levodopa is given in combination with other decarboxylase inhibitors. This can prevent levodopa from being converted before it reaches the brain.
Benefits of administering levodopa in combination with other decarboxylase inhibitors

The combined administration of the drugs mentioned can reduce the dose of levodopa by 75%. Because this is how the dopamine level in the brain can be stabilized.
Therefore, when combined with the other drugs, levodopa is clinically far more effective and the effect is also faster. Since less dopamine reaches the peripheral areas, the effects on the cardiovascular system and gastrointestinal tract are less. Levodopa is therefore always administered in combination with benserazide or carbidopa.
Conclusion
Levodopa is used as a first-line therapy for Parkinson’s disease. This drug is used in combination with other drugs to improve its effectiveness.
If you have any doubts or questions about this medicine, seek advice from your doctor or pharmacist and find out about the progress in clinical trials that make new therapies possible.