What Is Examined In A Urine Test?
With a urine test you can analyze different variables. The main goal is to determine the presence or absence of certain substances in the urine. Because this information is essential for a diagnosis.
A urine test is an examination that can help identify different types of health problems. The appearance, concentration and constituents of the urine are analyzed. The results may suggest a disease. Other methods are then used to confirm this suspicion.
It is important to make it clear that a urine test alone does not provide a definitive diagnosis. So it is up to a doctor to judge the results and their consequences. These types of tests are done to check for the presence of a disease. But also to be able to prevent it. Or watch their progress.
A urine test detects substances that the organism cannot hold back, or those that have to be eliminated. As little as 10 milliliters of urine can give clear indications of a number of diseases. These include, for example, diabetes, multiple myeloma and kidney failure.
Why do you take a urine test?
In general , your doctor will order a urine test for one of the following purposes :
- Assessment of the function of the kidneys: The concentration of the urine can be used to determine whether the kidney function is normal or not.
- Detection of germs: For example, if a urinary tract infection is suspected, a urine test is ordered. Because in this way it can be proven whether germs are present. In addition, the exact type of germs can also be determined by a subsequent urine culture.
- Detection of certain substances in the organism: There are substances that should not be present in the urine under normal conditions. If they do occur, they can be an indication of a health problem.
- Assessment of the effects of certain diseases or medications: A urine test can be used to determine whether certain substances are present in the organism and in what amount. Based on this information, the doctor can assess whether a disease has improved or worsened, or whether a drug has caused an undesirable side effect.
Types of urine tests
There are several ways to analyze urine, depending on the method used and the purpose of the test. The usual tests are as follows:
- Uroscopy: This is the observation and examination of the appearance of urine. The color, the cloudiness and the smell are particularly important. However, this type of analysis does not produce conclusive results.
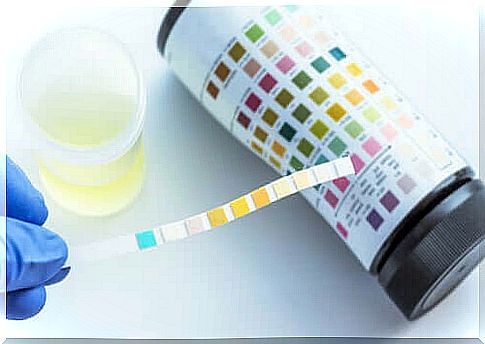
- Test strips: A small amount of urine is placed on a special strip with some chemical components. These react to the presence of certain substances in the urine. As a result, the strip changes color.
- Examination of the urine sediment: Such an analysis is carried out in the laboratory. First of all, the solid components present in the urine are separated from the liquid. Then you examine them under the microscope. In this way one can determine whether certain particles or cell elements are present.
- Biochemical analysis: This examination is also carried out in the laboratory. This makes it possible to determine whether certain substances or elements are present in the urine. And those that can indicate an illness. Such an analysis is very comprehensive. It is carried out by biochemists using special methods.
- Microbiological Study: This is a urine culture. This is used to detect infections. It can also be used to determine the germ on which it is based.
What are the results of a urine test?
A general urine test is usually done first. This is how you can identify any abnormalities in the appearance of the urine. Normal urine is clear and has little odor. Therefore, a cloudy appearance and a strong odor are indications that something is wrong.
A first test is then carried out with a test strip. A small amount of the urine is placed on the strip. If this does not change its color, it means that the urine is completely normal. However, if the color of the stripe changes, it means that there is a substance in the urine that should not be present.
This gives results for the following values:
- Acidity or pH: If this is not normal, it indicates problems in the urinary tract or kidneys.
- Concentration: A high concentration is a symptom of dehydration.
- Protein: The high presence of protein indicates kidney problems.
- Glucose: If there is glucose in the urine, it can indicate diabetes.
- Ketone bodies: These also indicate diabetes. In particular for faults that can be serious.
- Bilirubin: The presence of elevated bilirubin levels suggests the possibility of liver disease or damage.
- Blood: If blood is found in the urine, it can be a sign of an infection. Likewise for kidney damage or kidney stones. Or kidney or bladder cancer. So if there is blood in the urine, other methods should be used to arrive at a clear diagnosis.
- Nitrite content or presence of leukocytes: This is an indication of the presence of an infection.
If certain substances are detected in the urine, a more detailed laboratory analysis is necessary. Such as examinations of the urine sediment, biochemical analyzes or microbiological examination. The doctor always decides on the steps to be taken. It is important that you follow their instructions carefully. Because this is the only way they can help you with your complaints. And of course you should see your doctor immediately if you have any urinary tract problems.