Phlebitis: Description, Symptoms And Treatment
The main characteristic of phlebitis is the appearance of a clot in a vein or group of veins, be it superficial or internal. Treatment is usually fairly straightforward, should be done quickly, however.
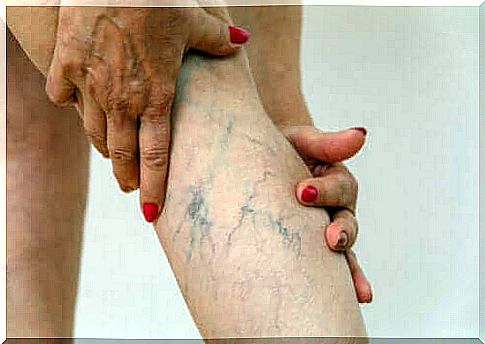
Phlebitis, also known as thrombophlebitis, is inflammation that results from the formation of a blood clot that blocks one or more veins, usually in the leg. There are two main types: superficial (near the outermost parts of the skin) and deep (within a muscle).
According to medical portals, superficial thrombophlebitis is a fairly common disease. It is estimated that 3 to 11% of the population will be affected at some point in their life before it. However, it is more common in women over the age of sixty.
Main symptoms of phlebitis
As mentioned earlier, there are two types of phlebitis: superficial and deep phlebitis. The latter is also known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The clinical signs vary by type. However, according to the US National Library of Medicine, common symptoms include the following:
- Swelling in the affected part of the body (usually the leg)
- Pain in the body area
- Reddened skin (not always)
- Warmth and softness over the blocked vein
In addition, superficial thrombophlebitis is manifested by red skin and the appearance of a pain-sensitive, hard red cord underneath. DVT, on the other hand, is less obvious, its main characteristics usually being pain and swelling.
Causes of Phlebitis
Phlebitis occurs when a blood clot lodges in one or more veins and causes swelling. The Mayo Clinic and other sources mentioned above have summarized the most common causes of this condition. This includes:
- An injury to the vein
- An inherited bleeding disorder
- Long immobility, such as those who are bedridden
- A pacemaker catheter that has pierced the vein (in the groin)
- Pregnancy and delivery in the last 6 months
- Obesity and overweight
In general, blood clots occur when something slows or changes the flow of blood in the veins. Any condition with this side effect (from obesity to certain types of surgery) could result in superficial or deep phlebitis.
diagnosis
A doctor can usually make a diagnosis based on the appearance of the affected area. However, if the cause of the phlebitis cannot be identified immediately, blood clotting tests such as venography (x-ray examination of the veins), genetic tests, and special ultrasound examinations must be carried out.
Risk groups and complications in phlebitis
As mentioned earlier, patients with phlebitis are on average over 60 years old and are mostly female. In addition, 90% of people with superficial thrombophlebitis have varicose veins. According to this, only 10% of the patients had previously healthy veins.
According to the AXA Healthkeeper Foundation, there are several risk factors that promote the development of phlebitis.
- Obesity puts you at risk of several heart diseases. Excessive body mass has been linked to cardiovascular disease, heart failure, or even sudden death, according to medical studies.
- Smoking encourages the formation of thrombi in arteries and veins.
- Hormone therapies such as contraceptives or hormone replacement pills increase the tendency for blood to clot in certain patients.
- Prolonged immobility due to hospitalization or a predominantly sedentary lifestyle.
In addition to these very common circumstances, a blood clot can also be favored by a family history of blood clotting disorders, a pacemaker, a past stroke and many other clinical pictures. Any disease that alters venous flow can lead to phlebitis.
As for the complications, early diagnosis of phlebitis allows for quick treatment. However, if left untreated, a blood clot could develop in the lungs, resulting in pulmonary embolism.
Treatment options
The angiologist and the vascular surgeon are responsible for treating phlebitis. Alternatively, in less severe cases, a family doctor should be able to prescribe analgesics, anticoagulants, or antithrombotics to break up the clot:
In more severe cases, surgical removal of the blocked vein may be considered if it is superficial. Alternatively, a doctor may place a venous bypass. However, these procedures are much rarer than the above.
Exercise can help prevent phlebitis
As you may have noticed, phlebitis is a fairly common condition, especially in older people with varicose veins in their legs. It is a condition with a positive prognosis, but it can get worse if not treated in a timely manner.
The best way to prevent phlebitis is to live a healthy lifestyle. So you should exercise, exercise, quit smoking, and eat healthily. You may not be aware of this, but many diseases are the result of being overweight. Thrombi are one of them.