Broad Spectrum Antibiotics: Effect And Resistance
Broad spectrum antibiotics are an important tool in the fight against various bacterial diseases. But they also have a very big disadvantage: bacteria often develop resistance!
Broad spectrum or broad spectrum antibiotics are capable of destroying a wide variety of bacteria. Find out interesting facts about these drugs today: How do they work and what are the consequences of misusing these drugs?
Interesting facts about broad spectrum antibiotics
As the name of these drugs already suggests, they work against a broad spectrum of bacteria, while antibiotics with a reduced spectrum only concentrate on one specific type of bacteria.
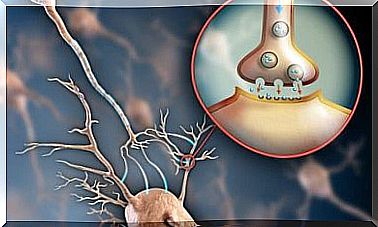
Most of these types of antibiotics are bacteriostatic, which means that they inhibit the growth or reproduction of bacteria, but do not kill dormant germs. This will make the harmful bacteria disappear. It does this by inhibiting protein synthesis in the bacteria, which stops growth.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics are very effective, but one of the problems with these drugs is that they not only eliminate pathogens, but also kill healthy endogenous bacteria in our intestinal flora.
There are a variety of antibiotics available. But time and again new antibiotic drugs have to be developed to replace older ones that are already ineffective. The problem of resistance, which bacteria develop over time, is also complicated.
Broad spectrum antibiotics: amoxicillin and clavulanic acid
These antibiotics work differently: they are a combination of two different ingredients. Amoxicillin prevents bacterial cell wall synthesis, while clavulanic acid improves the effectiveness of this substance by inhibiting an enzyme in bacteria that would otherwise break down the antibiotic.
It is a drug that is widely used. In particular, it is used for respiratory infections. However, because it is prescribed so frequently, bacteria resistance has also become very high and this has become a global health problem.
Tetracyclines
Tetracyclines are a number of active ingredients that share the same chemical structure and mechanism of action. They inhibit the protein synthesis of the bacteria and are used in particular when the causative agent of an infection is not yet known.
However, since this drug may have a toxic effect on the organism, its use is limited. It is usually used to treat chlamydia, brucellosis or mycoplasma.
Chloramphenicol
This medicine also inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. It is used in salmonella infections and also in some types of meningitis and pneumonia. However, this broad spectrum antibiotic affects the enzyme functions of the liver, so it must be used very carefully.
Macrolides
Although these drugs fight fewer bacteria, they are classified as broad-spectrum antibiotics. The prototype of a macrolide antibiotic is erythromycin, which also works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria.
This drug is considered to be less toxic. It is sometimes used for pneumonia caused by the bacteria Mycoplasma pneumonia or Legionella pneumophila .
Broad spectrum antibiotics: resistance
The misuse of broad-spectrum antibiotics thus becomes a particularly difficult problem. Since they cover a wide range of microorganisms, all of these bacteria can develop resistance. They can also develop insensitivity to several antibiotics. In this case, one speaks of multi-resistance.
Cross-resistance is also possible if bacteria develop insensitivity to two or more antibiotics that have a similar chemical structure or the same mode of action.
It is therefore of the utmost importance to educate the population about the consequences of incorrect use of antibiotics. The resistance is already having a very negative impact on world health and means that infections that could previously be treated can no longer be controlled.